Indexing
14. Indexing
Indexing mechanisms are used to speedup accesses to desired data.
Search Key is an attribute used to look up records. An index file consists of entries of form $\text{<search-key, pointer-to-record>}$. Note that binary tree is a very bad idea due to its large size.
There are 5 main metrics to evaluate an index: Efficiency, Access time, insertion time, deletion time and space overhead.
Ordered Indices
Index entries are stored in a sorted manner on the search key value. The index which specifies the order of the records is called the clustering index or the primary index. The search key of the primary index need not be the primary key. Other indices are called secondary indices.
A index is said to be dense if it appears for every search-key value in the file. Sparse index on the other hand contains records for only some search key values. We find the largest search key with value $<K$ and then search sequentially.
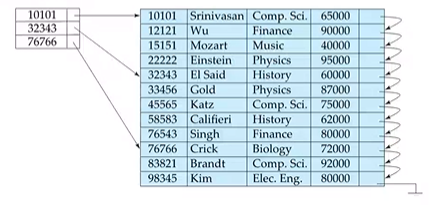
(something in the previous slide about how dense need not have entry per record?? in the below pic)
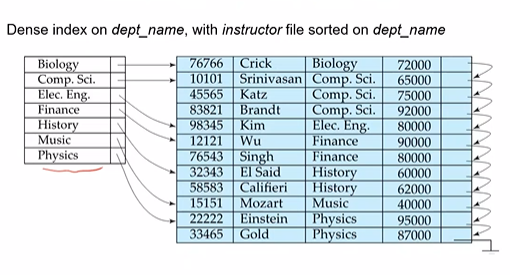
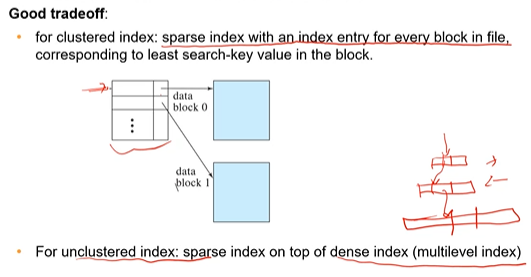
Skipped multilevel indexing, make notes on it!
B+ Tree Indexing
No duplicates is assumed. Each node can have varying number of children.
